Share this
blood microsampling device to monitor lead levels
by Neoteryx Microsampling on October 2,2023
September 2023 — The Centre de toxicologie du Québec (CTQ) announced that it is conducting a training mission to the country of Georgia on its innovative method of biomonitoring lead levels in children's blood using Mitra® microsampling devices. This innovative method of blood collection is an important component of the recently launched lead surveillance program in Georgia that aims to combat childhood lead exposure in the country.
Lead toxicity is considered one of the top 10 chemical elements of concern and is the underlying cause of 1 million annual deaths globally. Children, women of reproductive age, and people working in high-exposure environments are considered particularly vulnerable to high blood lead levels (BLL), which can cause numerous health problems. Early detection of BLL is critical to minimizing exposure and reducing potential long-term harm.
 As a mission with UNICEF, Anthony Breton, a master's student in chemistry at the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR), is introducing the National Center for Disease Control team in Georgia to the analysis of lead in blood samples collected with the Neoteryx Mitra-VAMS devices from Trajan Scientific and Medical.
As a mission with UNICEF, Anthony Breton, a master's student in chemistry at the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR), is introducing the National Center for Disease Control team in Georgia to the analysis of lead in blood samples collected with the Neoteryx Mitra-VAMS devices from Trajan Scientific and Medical.
This mission with UNICEF evolved out of a study that was launched by UQTR chemist and associate professor Ciprian Cirtiu, PhD, in 2019. That study aimed to replace traditional venipuncture (using a needle and syringe) blood collection methods with the portable and minimally invasive Mitra-VAMS device. Anthony Breton joined Dr. Cirtiu's team in 2021 to assist in this work, he is preparing his master's thesis on the use of Mitra-VAMS devices for the detection of metals in blood.
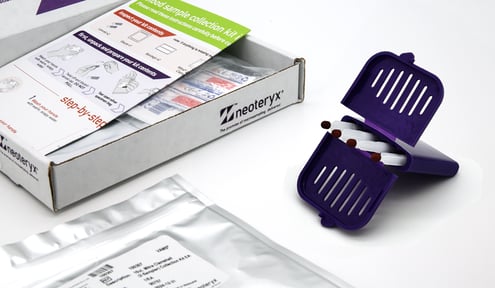
The Mitra device is small and easy to use by almost anyone. It is designed for quick and virtually painless blood collection using a lancet to prick a fingertip, heel, or other sampling site. This small microsampling device collects micro-sized blood samples and is much less invasive than a needle-based blood draw via venipuncture. The Mitra is ideally suited to collecting blood microsamples from children and other vulnerable patient populations.
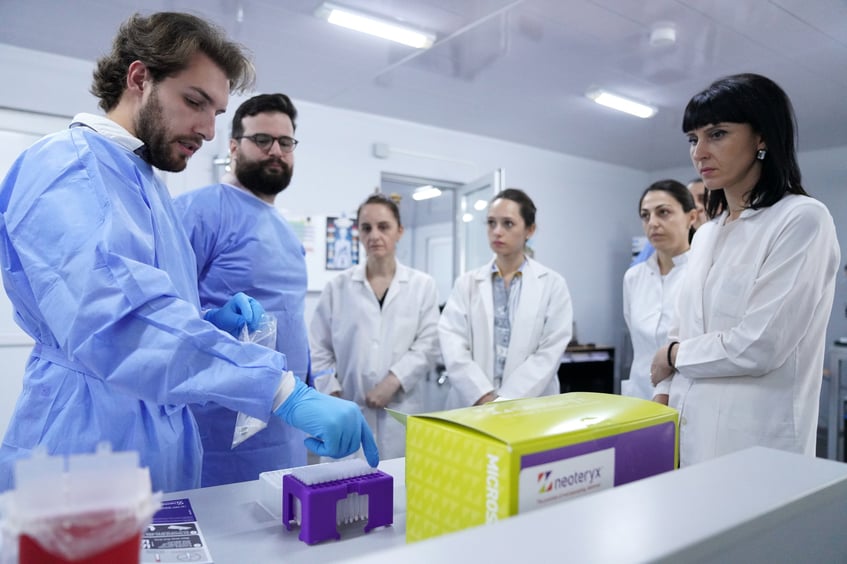 Caption: Lab Manager Tamar Jankhoteli and a team of researchers at the Chemical Risk-Factor Research Laboratory of the National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia receiving training from Antony Breton from INSPQ. UNICEF and the Government of Georgia have been actively cooperating on introduction of the lead surveillance system. Photo Credit: UNICEF/Geo-2023/Sukhitashvili
Caption: Lab Manager Tamar Jankhoteli and a team of researchers at the Chemical Risk-Factor Research Laboratory of the National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia receiving training from Antony Breton from INSPQ. UNICEF and the Government of Georgia have been actively cooperating on introduction of the lead surveillance system. Photo Credit: UNICEF/Geo-2023/Sukhitashvili
Breton and the team at CTQ successfully developed a method for the quantification of lead levels in whole blood sampled on Mitra® with VAMS® tips by inductively coupled plasma-MS/MS. Their method has shown excellent stability of lead in dried blood collected on Mitra devices and the method has minimized any lead contamination of the device tips.
According to the announcement from CTQ, Breton is training the Georgia team of scientists and clinicians on the lead quantification method and on how to use the sampling devices.
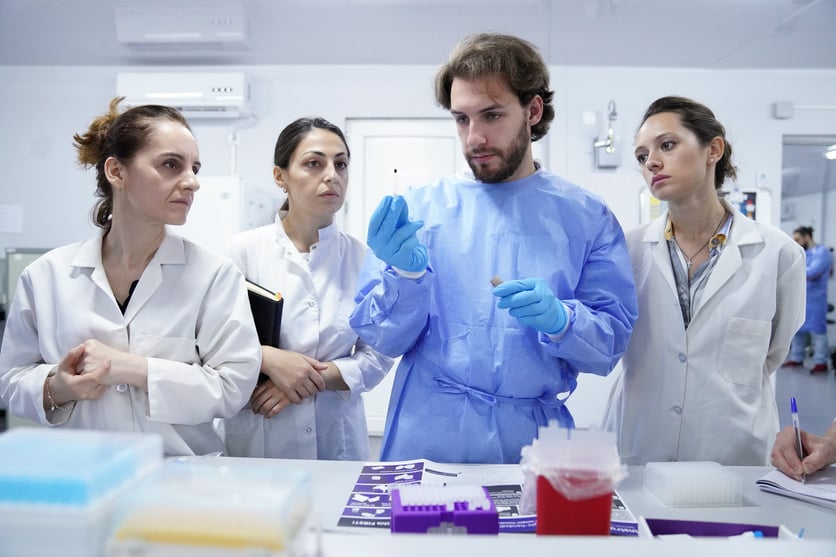

Caption: A team of researchers at the Chemical Risk-Factor Research Laboratory of the National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia being trained on using Mitra microsampling devices. UNICEF and the Government of Georgia have been actively cooperating on introduction of the lead surveillance system. Photo Credit: UNICEF/Geo-2023/Sukhitashvili
"I spent three days in Georgia showing people there how to use the Mitra-VAMS and explaining to them how to prepare the solutions and standards needed for testing," said Breton in the announcement.
"I implemented the analytical method developed in our laboratory on their instrument, which is similar to ours. I also trained them on the maintenance of induced plasma tandem mass spectrometry instruments, which are used for analysis."
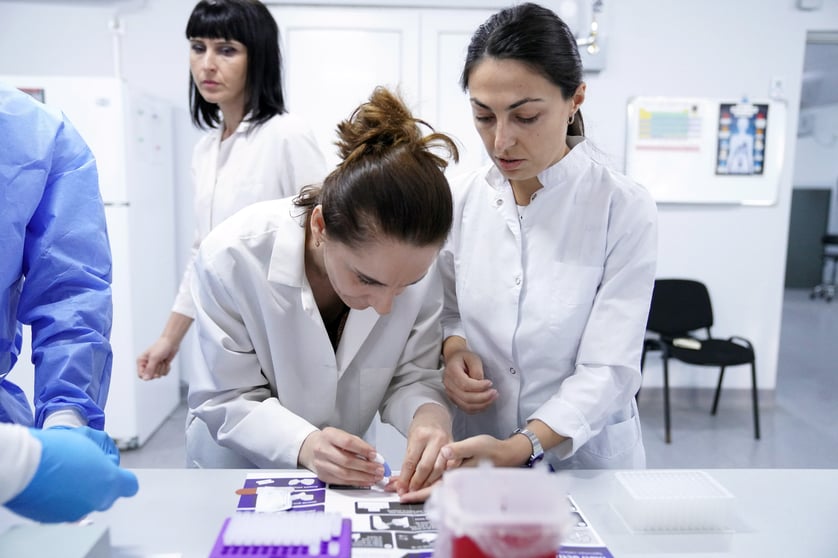 Caption: Lab Manager Tamar Jankhoteli and a team of researchers at the Chemical Risk-Factor Research Laboratory of the National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia practices finger-stick sampling with Mitra devices. UNICEF and the Government of Georgia have been actively cooperating on introduction of the lead surveillance system.
Caption: Lab Manager Tamar Jankhoteli and a team of researchers at the Chemical Risk-Factor Research Laboratory of the National Center for Disease Control and Public Health of Georgia practices finger-stick sampling with Mitra devices. UNICEF and the Government of Georgia have been actively cooperating on introduction of the lead surveillance system.
Photo Credit: UNICEF/Geo-2023/Sukhitashvili
The CTQ team has highlighted several advantages provided by the Mitra device, including the fact that it requires a smaller amount of blood for the same quality of results. In addition, they noted that Mitra microsamples can be stored at room temperature.
Further, the device doesn't require the intervention of a health professional to perform the sample collection. The group stated that these advantages make Mitra devices ideal for biomonitoring projects in areas far from urban centers, like the one in Georgia.
Breton added that the CTQ team wants to continue their research to expand the use of Mitra microsampling devices based on VAMS for the detection of other heavy metals and organic substances in the blood, such as perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
This is curated content. For more details about the important work being carried out by the Centre de toxicologie du Québec (CTQ) at the Institut national de santé publique du Québec (INSPQ) and in the field, please read their press release.
Related reading:
- Study Paper: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36891957/
- Study Summary by Neoteryx: https://www.neoteryx.com/microsampling-blog/monitoring-blood-lead-levels-using-vams
- For more information on using microsampling in toxicology studies, visit our "Microsampling for Toxicology" page.
Visit our Microsampling Resource Library to read about other innovative microsampling work:
Image Credits: UNICEF Georgia, INSPQ, CTQ, Trajan, Neoteryx
Share this
- Microsampling (41)
- Industry News, Microsampling News (37)
- Mitra® Device (34)
- Company Press Release, Product Press Release (22)
- Research, Remote Research (18)
- Infectious Disease, Vaccines, COVID-19 (15)
- Clinical Trials, Clinical Research (14)
- Biomonitoring, Health, Wellness (10)
- Blood Microsampling, Serology (10)
- Decentralized Clinical Trial (DCT) (8)
- Omics, Multi-Omics (7)
- Venipuncture Alternative (6)
- Skin Microsampling, Microbiopsy (5)
- Harpera Device (3)
- Specimen Collection (3)
- Toxicology, Doping, Drug/Alcohol Monitoring, PEth (3)
- Pharmaceuticals, Drug Development (2)
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, TDM (2)
- Antibodies, MAbs (1)
- Environmental Toxins, Exposures (1)
- Preclinical Research, Animal Studies (1)
- hemaPEN® Device (1)
- February 2026 (1)
- January 2026 (1)
- December 2025 (1)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- September 2024 (1)
- August 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (1)
- December 2023 (2)
- November 2023 (3)
- October 2023 (2)
- September 2023 (1)
- August 2023 (3)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (1)
- March 2023 (2)
- February 2023 (1)
- January 2023 (2)
- December 2022 (1)
- November 2022 (1)
- October 2022 (2)
- August 2022 (1)
- April 2022 (1)
- February 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (1)
- December 2021 (1)
- November 2021 (1)
- October 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (1)
- August 2021 (2)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (2)
- April 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (2)
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (1)
- December 2020 (1)
- November 2020 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- September 2020 (2)
- August 2020 (3)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (2)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (1)
- January 2019 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- July 2018 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (1)
- March 2017 (1)
- February 2017 (1)
- May 2016 (1)
- December 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (1)
- August 2015 (1)
- August 2014 (1)
- July 2014 (1)



No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think