Share this
therapeutic drug monitoring immunosuppressants: microsampling benefits
by Neoteryx Microsampling on Jan 14, 2020 4:43:00 AM
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM) is pivotal after tissue or organ transplantation, especially with the intricacies of immunosuppressants (ISPs). Traditional methods, which utilize whole blood specimens, unfortunately, have shortcomings, like weaker correlation with drug concentrations and the invasiveness of drawing wet blood samples.
Evolution of Sampling Methods

While the medical community realized the drawbacks of wet blood samples, innovations brought forth capillary dried blood microsampling. Instead of requiring large volumes of liquid blood, only a finger-stick is needed to draw a small, low-volume sample. The drawn blood then dries and is analyzed in labs through advanced methods such as LC-MS/MS. Though effective, this method has its challenges, notably the matrix effect that can skew results.
Alternative TDM methods surfaced, including the use of oral fluids, but they too had their pitfalls. Issues like contamination became major roadblocks.
Dried blood spot (DBS) sampling emerged as a promising alternative. However, its efficacy was diminished by factors like the hematocrit effect.
The Dawn of Volumetric Microsampling
The latest in this evolution is volumetric microsampling, specifically "volumetric absorptive microsampling." Unlike prior methods, hematocrit effects don’t hinder its performance. Devices designed for this method ensure a consistent blood volume regardless of hematocrit.

The Mitra® device with VAMS® technology stands out. It rapidly absorbs the precise blood volume, which can then be sent to labs for detailed analysis.
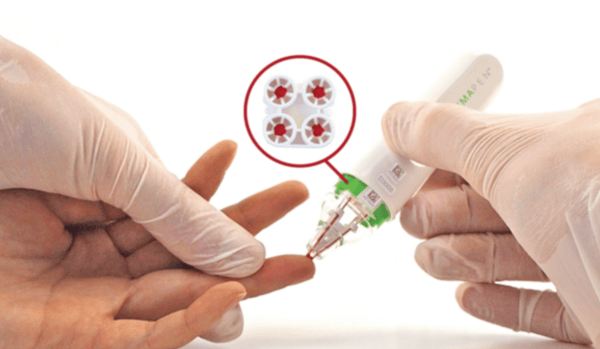
The hemaPEN® offers another approach, integrating capillary blood and DBS sampling. It takes four identical samples from one finger-stick, ensuring consistent volume and secure storage.
Microsampling devices like Mitra are game-changers. Patients can self-collect samples from the comfort of their homes, sending them to labs without frequent clinic visits.
Microsampling: A New Age in TDM
The rise of microsampling-based TDM offers more accurate ISP monitoring and presents clear advantages over traditional methods. Notably, for patients who are bedridden or in remote locations, home sampling is a boon.
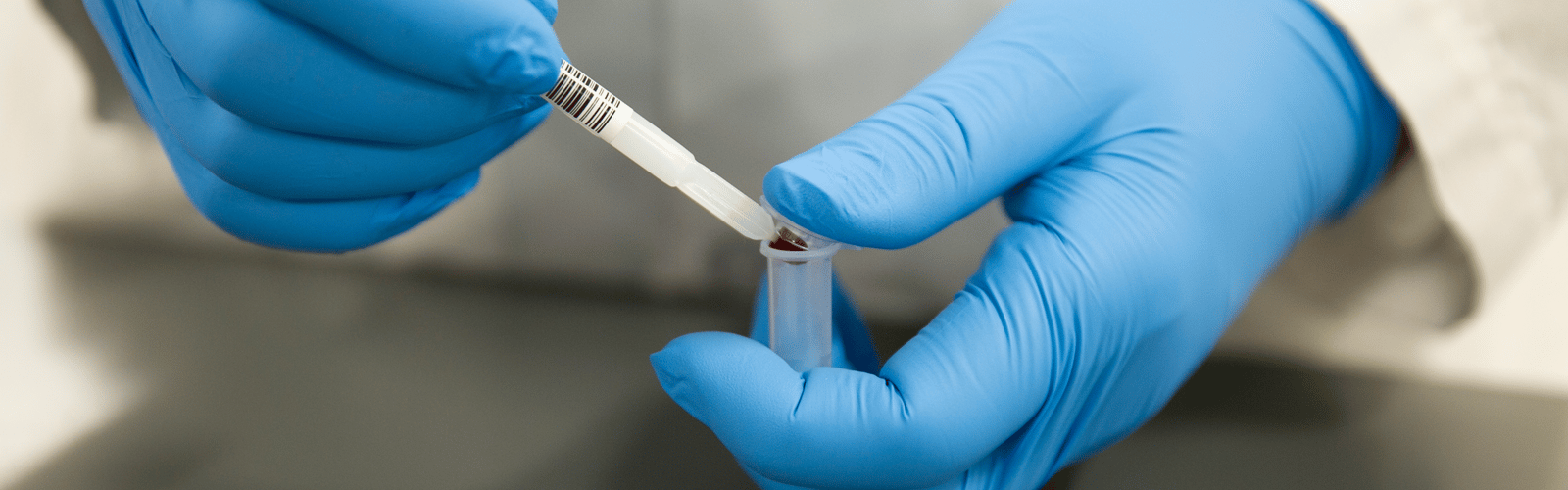
However, a word of caution to medical professionals: Proper patient training is essential for optimal remote sampling. And post-collection, correct handling and storage are critical for accurate results. To aid in this, the Neoteryx team at Trajan Scientific and Medical offers a plethora of resources and support.
Visit our Resources tab to find the instructions, videos and other resources you need for Mitra devices and hemaPEN devices.
More information about remote microsampling for TDM can be found via our Microsampling for Drug Monitoring page.
For case studies and peer-reviewed publications and other resources, please visit our Technical Resource Library.
Image credits: Trajan, Neoteryx, iStock

Share this
- Microsampling (206)
- Research, Remote Research (119)
- Venipuncture Alternative (105)
- Clinical Trials, Clinical Research (83)
- Mitra® Device (73)
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, TDM (51)
- Dried Blood Spot, DBS (39)
- Biomonitoring, Health, Wellness (30)
- Infectious Disease, Vaccines, COVID-19 (24)
- Blood Microsampling, Serology (23)
- Omics, Multi-Omics (21)
- Decentralized Clinical Trial (DCT) (20)
- Specimen Collection (18)
- Toxicology, Doping, Drug/Alcohol Monitoring, PEth (17)
- Skin Microsampling, Microbiopsy (14)
- hemaPEN® Device (13)
- Preclinical Research, Animal Studies (12)
- Pharmaceuticals, Drug Development (9)
- Harpera Device (7)
- Industry News, Microsampling News (5)
- Antibodies, MAbs (3)
- Company Press Release, Product Press Release (3)
- Environmental Toxins, Exposures (1)
- July 2025 (1)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (2)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (1)
- October 2024 (3)
- September 2024 (1)
- June 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (1)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (1)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (4)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (3)
- October 2023 (3)
- September 2023 (3)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- January 2023 (3)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (3)
- August 2022 (5)
- July 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (2)
- May 2022 (4)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (3)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (5)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (4)
- July 2021 (4)
- June 2021 (4)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (4)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (5)
- October 2020 (4)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (3)
- July 2020 (6)
- June 2020 (4)
- May 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (6)
- February 2020 (3)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (5)
- November 2019 (4)
- October 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (7)
- May 2019 (6)
- April 2019 (5)
- March 2019 (6)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (8)
- December 2018 (3)
- November 2018 (4)
- October 2018 (7)
- September 2018 (6)
- August 2018 (5)
- July 2018 (8)
- June 2018 (6)
- May 2018 (5)
- April 2018 (6)
- March 2018 (4)
- February 2018 (6)
- January 2018 (4)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (3)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (4)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (4)
- June 2017 (5)
- May 2017 (6)
- April 2017 (6)
- March 2017 (5)
- February 2017 (4)
- January 2017 (1)
- July 2016 (3)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (2)


No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think