Share this
patient-centric sampling in Poland: two case studies
by James Rudge, PhD, Technical Director, Trajan on Dec 26, 2023 9:00:00 AM
A company called LabExperts and their collaborators in Poland published two key posters on the analysis of drugs from blood samples collected using Mitra® devices based on VAMS® technology. The posters describe successful validations for two different and highly relevant applications of dried blood microsampling.
The first poster demonstrates a method for the sensitive multiplex detection of 27 drugs of abuse and their metabolites in line with published cut-offs from the DRUID (driving under the influence of alcohol and medicines) study. The second poster reports on a research and development project (CardioCarePack) to monitor drug levels among patients taking medication for cardiac arrhythmias.
This blog reviews the processes and outcomes of both posters from LabExperts...
Research Poster 1: Microsampling for DRUID Monitoring
The European Union’s Research on Driving Under the Influence of Drugs, Alcohol and Medicines — the DRUID Project.
The DRUID project was commissioned by the European Union in 2007 to help to standardize regulations on the analysis of biological samples collected from people who were driving under the influence. This project examined a range of experimental, epidemiological and related studies which took place across 18 countries over 5 years, producing over 50 reports. Among the many findings gathered via tests performed on 50,000 drivers in13 countries across Europe, alcohol was present in 3.48%, and illicit drugs were present in 1.9%.
The final DRUID report (published in 2012) also discussed the advantages of using dried blood spot (DBS) sampling with a finger-prick instead of traditional whole blood sampling with venipuncture to screen for these substances. The report included the following statement:
“The evaluation data showed no significant differences in precision: all substances investigated in the presented studies could be determined in a DBS as reliably as in a whole blood specimen. Thus, the project demonstrated that DBS drug analysis can be regarded as a valuable and inexpensive alternative to the determination of substances in whole blood. Such use of DBS could greatly facilitate blood analysis in drug-driving cases in the near future.”
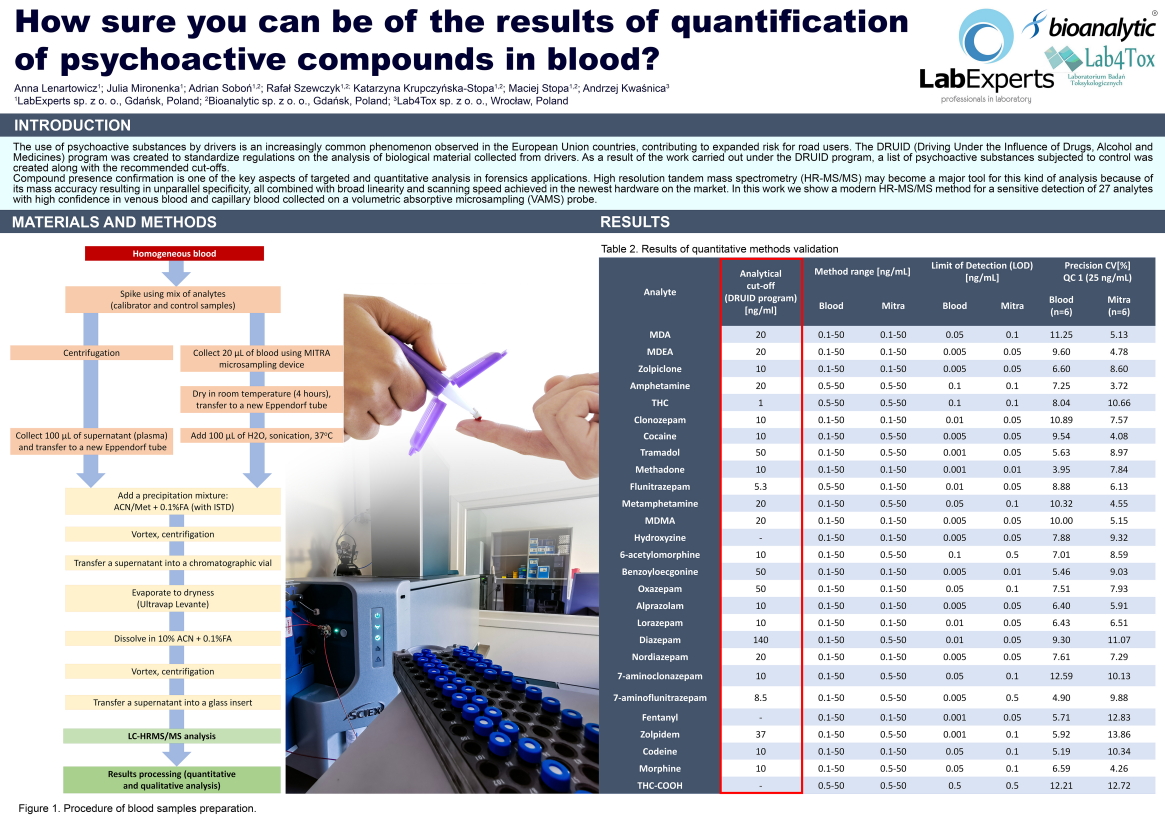
A poster was presented at the IATDMCT 2023 meeting entitled “How sure can you be of the results of quantification of psychoactive compounds in blood?” by Anna Lenbartowtiz et al at three companies: LabExperts sp. Z o. o, Bioanalytic sp. Z o. o, and Lab4Tox sp. Z o. o in Poland. The poster reported on validating an LC-MS/MS assay to measure 27 analytes listed in the DRUID program report.
From this validated assay they achieved limit of detection (LODs) below the analytical cut-off for all analytes listed. They also obtained linearity of R ≥ 0.995, a working range of 0.1/0.5-50 ng mL, repeatability of ≤ 15% CV, and accuracy of ≤ 80-120%. This was achieved using 20 µL Mitra® devices based on VAMS® technology and comparing dried blood samples collected with these devices to traditionally collected plasma samples.
Conclusion on the DRUID Study Poster
Given the many reported benefits the Mitra microsampling method has over the DBS method in terms of analytical performance, user experience and sample quality, Anna Lenbartowtiz et al demonstrated excellent analytical performance from Mitra extracts. As a result, we can imagine that Mitra could be used instead of DBS as a more effective tool in monitoring people who may be driving under the influence of drugs and/or alcohol.
Research Poster 2: CardioCarePack
Improving the lives of patients suffering from cardiac arrythmias
Cardiac arrythmia, which affects 12.6% of people over the age of 65, can be a fatal condition, accounting for around 80% of sudden cardiac deaths. Cardiac arrythmia describes perturbations in the normal heart rhythm / rate. This results in reduced oxygenated blood circulating through the body, leading to dizziness and fainting. If left untreated, the condition can lead to stroke, cardiomyopathy, cardiac arrest and, ultimately, death. Thankfully, there are several treatments for cardiac arrythmia, such as pacemakers, as well as non-invasive pharmaceutical treatments, including sodium channel blockers, beta blockers, potassium channel blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of certain medications is an important component in the care plan for patients taking such drugs. The benefits of TDM include improved self-reported drug adherence in transplant patients, as one example. In a poster presented by Maciej Stopa et al at the ASMS 2023 meeting, the group highlighted that TDM is also important in the following scenarios:
- narrow therapeutic windows
- risk of serious drug reactions
- long elimination times
- formation of metabolites, which can be pharmacologically active [v].
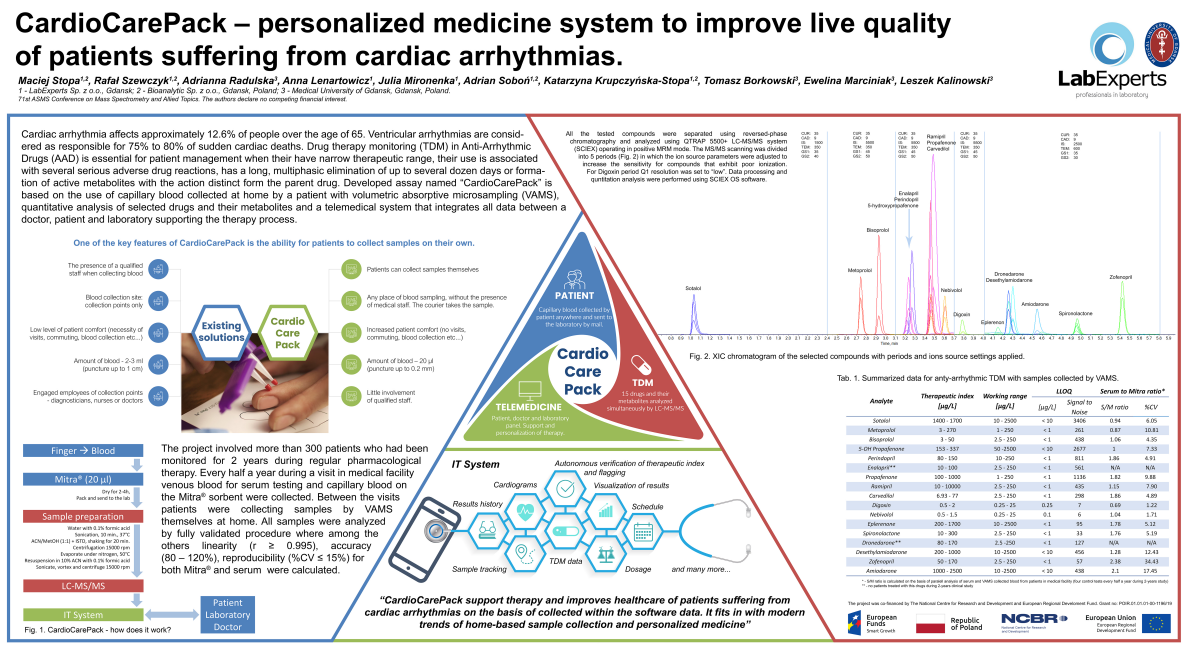
The CardioCarePack
The poster by Maciej Stopa et al from 3 institutions in Poland is entitled “CardioCarePack – personalized medicine system to improve live [life] quality of patients suffering from cardiac arrhythmias.” It reports on a successful 2-year study monitoring 300 patients receiving drug treatment for cardiac arrhythmias. The study highlights a successful validated method for measure 15 drugs used to treat this cardiac condition. During the study, paired capillary blood using Mitra and venous blood (for serum conversion) was collected every 6 months, where serum to Mitra ratios were evaluated for the drugs tested.
The poster also introduced the CardioCarePack, which explored the use of at-home patient sampling with Mitra coupled with a smartphone app. Features of the smartphone app included sample tracking, results history (TDM and Cardiograms), autonomous verification of therapeutic index tracking / flagging, and dosing.
The researchers used the LC-MS/MS method to measure 15 drugs and their metabolites.
Conclusion on the CardioCarePack Study Poster
We are beginning to see a trend in combining home sample collection with digital apps and other digital health solutions. From smartwatches to phone apps, these solutions are designed to track or augment data, from measuring blood sugars to biomarkers, and acting as early warning systems of impending health issues. These digital technologies, coupled with remote blood sampling, can help care providers to monitor drug levels as a remote telehealth complement traditional care pathways. As we move towards longitudinal personalized healthcare, well-care solutions such as the CardioCarePack will be vital to enable this advancement.
The work conducted by LabExperts and their collaborators shows two excellent use-case scenarios where remote sampling assists in furthering the field and, hopefully, improving lives.
View the DRUID poster here.
View the CardioCarePack poster here.
Explore microsampling information and frequently asked questions: 

Image Credits: LabExperts, Bioanalytic
Share this
- Microsampling (206)
- Research, Remote Research (119)
- Venipuncture Alternative (105)
- Clinical Trials, Clinical Research (83)
- Mitra® Device (73)
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, TDM (51)
- Dried Blood Spot, DBS (39)
- Biomonitoring, Health, Wellness (30)
- Infectious Disease, Vaccines, COVID-19 (24)
- Blood Microsampling, Serology (23)
- Omics, Multi-Omics (21)
- Decentralized Clinical Trial (DCT) (20)
- Specimen Collection (18)
- Toxicology, Doping, Drug/Alcohol Monitoring, PEth (17)
- Skin Microsampling, Microbiopsy (14)
- hemaPEN® Device (13)
- Preclinical Research, Animal Studies (12)
- Pharmaceuticals, Drug Development (9)
- Harpera Device (7)
- Industry News, Microsampling News (5)
- Antibodies, MAbs (3)
- Company Press Release, Product Press Release (3)
- Environmental Toxins, Exposures (1)
- July 2025 (1)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (2)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (1)
- October 2024 (3)
- September 2024 (1)
- June 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (1)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (1)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (4)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (3)
- October 2023 (3)
- September 2023 (3)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- January 2023 (3)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (3)
- August 2022 (5)
- July 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (2)
- May 2022 (4)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (3)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (5)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (4)
- July 2021 (4)
- June 2021 (4)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (4)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (5)
- October 2020 (4)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (3)
- July 2020 (6)
- June 2020 (4)
- May 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (6)
- February 2020 (3)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (5)
- November 2019 (4)
- October 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (7)
- May 2019 (6)
- April 2019 (5)
- March 2019 (6)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (8)
- December 2018 (3)
- November 2018 (4)
- October 2018 (7)
- September 2018 (6)
- August 2018 (5)
- July 2018 (8)
- June 2018 (6)
- May 2018 (5)
- April 2018 (6)
- March 2018 (4)
- February 2018 (6)
- January 2018 (4)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (3)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (4)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (4)
- June 2017 (5)
- May 2017 (6)
- April 2017 (6)
- March 2017 (5)
- February 2017 (4)
- January 2017 (1)
- July 2016 (3)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (2)

No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think