Share this
4 alternatives to dried blood spot cards
by Neoteryx Microsampling on Mar 21, 2017 6:57:00 AM
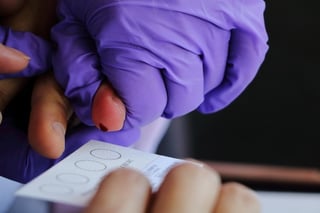 Dried blood spot (DBS) blood collection techniques have long been useful in blood analysis research. DBS cards can reduce costs, and they provide ethical advantages and higher sample retention.
Dried blood spot (DBS) blood collection techniques have long been useful in blood analysis research. DBS cards can reduce costs, and they provide ethical advantages and higher sample retention.
However, DBS cards are not without limitations. Hematocrit level, blood viscosity, analyte nature, and sampling conditions all affect the blood sample analysis, particularly from an analytical standpoint.
Any thoughtful consideration of DBS techniques includes exploring popular alternatives. Here are four you should know about.
Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME)
Solid phase microextraction is a sample preparation method that is based on the differential migration of analytes from the sample fluid into the stationary phase: the functionalized silica particles, coated on a BioSPME metal fiber. The method is viable for direct sampling of whole blood, and also for urine, saliva, and tissue.
SPME technique combines sampling, sample preparation, and extraction in one step, reducing blood handling, as well as increasing speed, improving efficiency, and boasting high sensitivity, especially in regard to the influence of blood hematocrit on analysis.
The efficiency of the method is, however, still affected by sample properties. And while SPME is suitable for on-site use, the whole process, unlike DBS, needs to be carried out by trained medical personnel.
Pre-cut Dried Blood Spot (PCDBS)
Another technique that was developed to reduce the limitations of DBS, mainly the impact of hematocrit, is pre-cut dried blood spot (PCDBS) microsampling. Instead of using a partial, fixed-sized punch from a DBS sample, PCDBS is based on the whole sample analysis through accurate volumetric applications of blood onto a pre-punched disc. Other advantages of this sampling method include 100 percent sample utilization, further reducing the needed volume of blood and elimination of carryover concerns related to DBS sample punching workflow.
While well-suited for use in a controlled setting, the PCDBS technique is not yet viable for patient self-sampling situations due to a defined volume of blood required.
Dried Plasma Spot (DPS)
With the development of multi-layer collection membranes, the dried plasma spot (DPS) microsampling technique is carried out with ease and comfort of DBS, without the drawbacks of SPME and PCDBS (no need for a controlled environment), as well as challenges of whole blood analysis (impact of hematocrit).
The technology utilizes a two-layer sampling card, consisting of a separation and a collection polymeric membrane. The plasma from a drop of blood from a finger-stick prick can flow through the separation membrane, forming a plasma spot on the bottom collection membrane after the top layer is peeled off.
Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling
Volumetric absorptive microsampling is a technique that allows the collection of volumetrically accurate samples of blood without the need for specialized devices.
The Mitra® device consists of a plastic handle with an absorbent VAMS® tip, with highly reproducible internal porous volume. The VAMS tip, when dipped into the sample, wicks up an accurate volume of blood independently of hematocrit. The whole VAMS tip is extracted without manipulation, providing further advantages over DBS (no punching), while still being fully viable in self-sampling or low-resource scenarios.
The method is also compatible with tip-based automation systems, making it an increasingly fruitful sampling technique from an analytical point of view.
Share this
- Microsampling (206)
- Research, Remote Research (119)
- Venipuncture Alternative (106)
- Clinical Trials, Clinical Research (83)
- Mitra® Device (73)
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, TDM (51)
- Dried Blood Spot, DBS (39)
- Biomonitoring, Health, Wellness (30)
- Infectious Disease, Vaccines, COVID-19 (24)
- Blood Microsampling, Serology (23)
- Omics, Multi-Omics (21)
- Decentralized Clinical Trial (DCT) (20)
- Specimen Collection (18)
- Toxicology, Doping, Drug/Alcohol Monitoring, PEth (17)
- Skin Microsampling, Microbiopsy (14)
- hemaPEN® Device (13)
- Preclinical Research, Animal Studies (12)
- Pharmaceuticals, Drug Development (9)
- Harpera Device (7)
- Industry News, Microsampling News (5)
- Antibodies, MAbs (3)
- Company Press Release, Product Press Release (3)
- Environmental Toxins, Exposures (1)
- July 2025 (1)
- May 2025 (1)
- April 2025 (2)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (1)
- October 2024 (3)
- September 2024 (1)
- June 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (1)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (1)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (4)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (3)
- October 2023 (3)
- September 2023 (3)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- January 2023 (3)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (3)
- August 2022 (5)
- July 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (2)
- May 2022 (4)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (3)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (5)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (4)
- July 2021 (4)
- June 2021 (4)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (4)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (5)
- October 2020 (4)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (3)
- July 2020 (6)
- June 2020 (4)
- May 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (6)
- February 2020 (3)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (5)
- November 2019 (4)
- October 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (7)
- May 2019 (6)
- April 2019 (5)
- March 2019 (6)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (8)
- December 2018 (3)
- November 2018 (4)
- October 2018 (7)
- September 2018 (6)
- August 2018 (5)
- July 2018 (8)
- June 2018 (6)
- May 2018 (5)
- April 2018 (6)
- March 2018 (4)
- February 2018 (6)
- January 2018 (4)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (3)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (4)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (4)
- June 2017 (5)
- May 2017 (6)
- April 2017 (6)
- March 2017 (5)
- February 2017 (4)
- January 2017 (1)
- July 2016 (3)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (2)



Comments (1)