DBS Technology: Microsampling Capillary Blood
Blood microsampling presents a promising alternative to traditional venous blood draws, with several key advantages that make it particularly appealing for various medical research scenarios:

Remote & Decentralized Sampling:
This method allows for blood collection at home or in remote locations without the need for specialized medical staff, potentially improving participant compliance and retention.
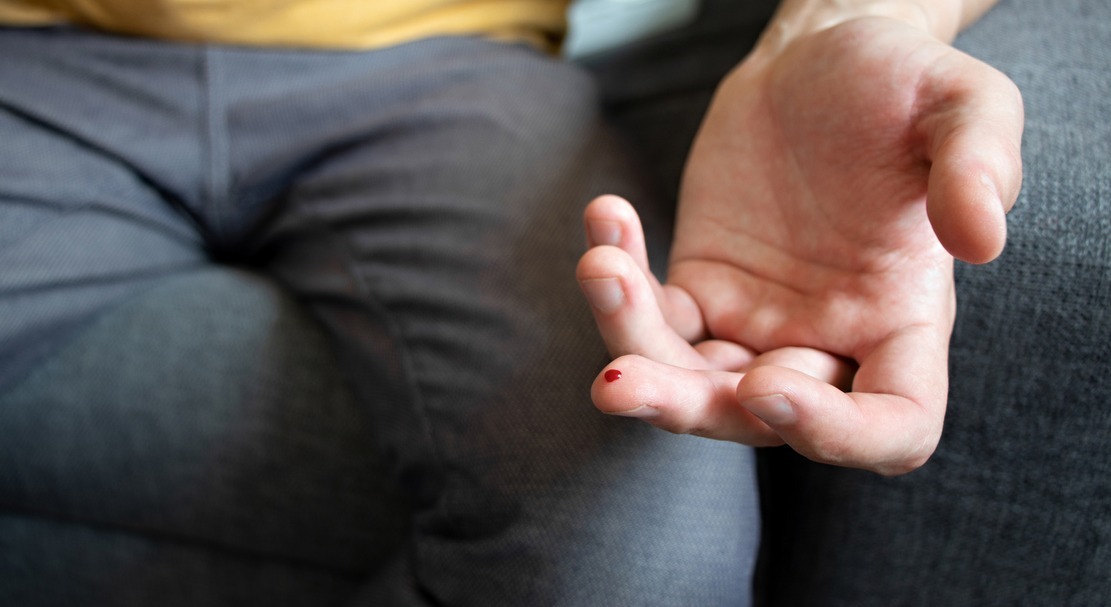

Minimally Invasive & Patient-Friendly:
Microsampling requires only small-volume blood collection through methods like finger-sticks or heel-sticks, which can reduce patient anxiety and discomfort. This feature may enhance participant adherence, especially in pediatric or long-term studies.
/2022%20Mitra%20Lifestyle%20Images%20(approved)/mailing-no-cold-chain-2-1.jpeg?width=900&height=480&name=mailing-no-cold-chain-2-1.jpeg)
Efficient & Cost-Effective Collection:
Compared to conventional blood sampling methods, microsampling typically involves minimal preparation, storage, and transportation logistics, which can lower overall project costs.

Ethically Conscious Research:
The reduced blood volume required for microsampling can significantly minimize health risks and enhance ethical compliance, making it especially valuable in pediatric studies, research involving vulnerable populations, and animal studies.
Understanding Hematocrit: A Key Challenge in Microsampling

Hematocrit, which refers to the proportion of blood made up of red blood cells, can significantly affect the accuracy of traditional dried blood spot (DBS) methods. Variations in hematocrit levels, whether higher or lower, can result in inconsistent outcomes, complicating the interpretation of important biomarkers.
Recent advancements in blood microsampling technology aim to address these hematocrit-related issues, offering more accurate and reproducible results across a range of hematocrit levels.
/Mitra_Media%20Library%20Images%20(March-April%202023)/blood-sample-collection-1.jpeg?width=1111&height=725&name=blood-sample-collection-1.jpeg)
How VAMS® Technology Can Address the Hematocrit Challenge
Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling (VAMS®), demonstrated by the Mitra® device, marks a significant advancement in capillary sampling. This innovative technique allows for the precise collection of blood volumes that remain unaffected by variations in hematocrit levels. Here are several potential advantages of this approach:
Volumetric Precision:
Reliable Analysis:
Simplified Workflow:
Enhanced Stability:
VAMS Across Industries: Reliable, Compliant, and Proven.
Blood microsampling is transforming diverse fields; its value is widely recognized through extensive third-party research and clinical validation:

Clinical Trials
Streamlined, patient-friendly blood sampling can increase participant retention and simplify trial logistics.

Pediatrics & Neonatology
Reduced blood volume requirements potentially minimize risks for young participants.

Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM)
Accurate, repeated sampling without venipuncture discomfort.

Population Health Studies
Easy remote sampling, potentially improving participation in large-scale studies.
Veterinary & Preclinical Research
Ethical sampling methods help comply with the "3Rs" (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) principles in animal research.
The Mitra® device, leveraging advanced VAMS® technology, provides researchers with a robust, compliant microsampling solution, meeting rigorous industry and regulatory standards, while delivering reliability, ease of implementation, and ethical integrity.
Explore Microsampling for Your Research
Is microsampling the right fit for your project? Explore how adopting microsampling technology could enhance your research's effectiveness, ethical compliance, and participant engagement. Contact us today to discuss your project's eligibility for blood microsampling solutions.
Sales:
neo.sales@trajanscimed.com
Technical Support:
neo.support@trajanscimed.com
Customer Service:
neo.cs@trajanscimed.com
US | 6:00 am - 5:00 pm PST
tel: +1 (310) 787-8747
UK | 08:30 - 05:00 GMT (M-Th)
UK | 08:30 - 04:00 GMT (Fri)
tel: +44 1908 568844
Fax Number: +1 (310) 787-8770
