Share this
5 remote patient monitoring devices and the future of healthcare
by Neoteryx Microsampling on Dec 3, 2019 12:03:00 AM
The capabilities of remote patient monitoring devices and technologies have become more powerful, effective, and interesting than ever before.
 According to IHS (Information Handling Services), more than four million patients monitored their health conditions remotely in 2020, and that is a 34% increase in remote patient monitoring (RPM) and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) since 2014.
According to IHS (Information Handling Services), more than four million patients monitored their health conditions remotely in 2020, and that is a 34% increase in remote patient monitoring (RPM) and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) since 2014.
Technological giants such as Google, Apple, and Amazon are tapping into the RPM market; this leads to drastic changes in healthcare. RPM technologies have increased the quality of life, reduced clinic visits and hospitalizations, and shortened hospital stays. And more companies entering the market by introducing and upgrading RPM devices.
Here are 5 remote patient monitoring devices to watch:
1. Microsampling Devices
 Already on the market for several years, there are hand-held devices like the Mitra® device and hemaPEN® can be used to simplify blood collection for patients at home.
Already on the market for several years, there are hand-held devices like the Mitra® device and hemaPEN® can be used to simplify blood collection for patients at home.
Thanks to a simple finger-stick method using a lancet, blood collection with both the Mitra and the hemaPEN is less invasive than traditional blood collection methods.
These devices can be used by a nurse or other healthcare professional with minimal training, or by a layperson at home, who is following illustrated step-by-step instructions and "how to" videos.
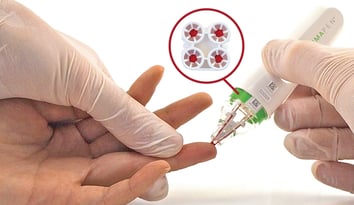 Additionally, these remote sampling technologies are precise, reliable and cost-effective, making them well-suited to collecting blood samples in low-resource regions. Microsampling devices are being used in remote research, toxicology studies, clinical trials, and therapeutic drug monitoring programs, to name a few areas where its adoption is accelerating.
Additionally, these remote sampling technologies are precise, reliable and cost-effective, making them well-suited to collecting blood samples in low-resource regions. Microsampling devices are being used in remote research, toxicology studies, clinical trials, and therapeutic drug monitoring programs, to name a few areas where its adoption is accelerating.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
DexCom™ was the first company to develop continuous glucose sensing technologies. Dexcom G6 eliminates the need to make finger pricks for glucose testing. Patients can now monitor their blood sugar levels throughout the day and night using a sensor inserted under the skin.
A more advanced version of the device has been released. The San Diego-based company has partnered with Apple to connect the Apple Watch with its CGM sensor. DexCom’s upgraded device was released in early 2020.
3. Surgical Robotics
Surgical robotics are designed to help surgeons perform complex procedures with greater skill, acuity and precision. For example, the rotation of a human wrist is limited, which restricts a surgeon's access to hard-to-reach places during certain procedures in delicate areas of the body. The fully reticulated instruments of surgical robotics, however, can be controlled by a robotics-trained surgeon to allow greater access with greater acuity.
A surgeon's visualization of the surgical area is also greatly improved with the assistance of surgical robotics, which can provide 3-dimensional views in magnification projected on a wide screen in the operating room. While it is unlikely that surgical robots will replace human surgeons, the smart technology and advanced instrumentation they provide can enhance the performance of an already skilled surgeon.
The high price of in-demand robotics has been the biggest hindrance faced by health organizations. Several companies are developing more affordable surgical robotics systems. Riverfield™, a Japanese startup, launched a low-priced surgical robot in 2020. However, Intuitive Surgical, Stryker Inc., and Medtronic continue to lead in the surgical robotics market.
4. AI-backed Computer Vision
Artificial intelligence (AI) has advanced many industries, including healthcare. In 2020, it is expected to enhance computer vision. This technology will enable devices to make accurate diagnoses faster than humans. An example of its application is estimating blood loss in mothers during and after childbirth.
This application of AI-enabled technology may help hospitals meet a new requirement made by The Joint Commission, which accredits roughly 77% of hospitals in the United States. In 2019, the Commission announced a new perinatal safety guideline requiring accredited hospitals to take measures to more closely monitor and treat postpartum patients who experience maternal hemorrhage. The new standard went into effect in July 2020. AI-enabled platforms that support this effort are being developed by companies like Gauss.
5. Mixed Reality Surgical Devices
Mixed reality is a combination of virtual and augmented realities. It enables the interaction of digital objects while creating a sense of presence in the real world. When applied to the medical field, mixed reality devices help medical professionals better understand and visualize a patient’s condition. For example, physicians can gather important, current imaging information before beginning a surgical procedure.
More information about remote microsampling for TDM can be found via our Microsampling for Drug Monitoring page.
Image Credtis: Trajan, Neoteryx, Shutterstock
Share this
- Microsampling (205)
- Research, Remote Research (118)
- Venipuncture Alternative (106)
- Clinical Trials, Clinical Research (82)
- Mitra® Device (72)
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, TDM (50)
- Dried Blood Spot, DBS (38)
- Biomonitoring, Health, Wellness (31)
- Infectious Disease, Vaccines, COVID-19 (24)
- Decentralized Clinical Trial (DCT) (22)
- Blood Microsampling, Serology (21)
- Omics, Multi-Omics (19)
- Specimen Collection (17)
- Toxicology, Doping, Drug/Alcohol Monitoring, PEth (17)
- hemaPEN® Device (13)
- Preclinical Research, Animal Studies (12)
- Pharmaceuticals, Drug Development (9)
- Harpera® Tool (5)
- Industry News, Microsampling News (5)
- Skin Microsampling, Microbiopsy (5)
- Company Press Release, Product Press Release (4)
- Antibodies, MAbs (3)
- Environmental Toxins, Exposures (1)
- April 2024 (3)
- March 2024 (1)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (4)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (3)
- October 2023 (3)
- September 2023 (3)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- January 2023 (3)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (3)
- August 2022 (5)
- July 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (2)
- May 2022 (4)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (3)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (5)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (5)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (4)
- July 2021 (4)
- June 2021 (4)
- May 2021 (4)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (4)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- November 2020 (5)
- October 2020 (4)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (3)
- July 2020 (6)
- June 2020 (4)
- May 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (6)
- February 2020 (3)
- January 2020 (4)
- December 2019 (5)
- November 2019 (4)
- October 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (5)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (7)
- May 2019 (6)
- April 2019 (5)
- March 2019 (6)
- February 2019 (5)
- January 2019 (8)
- December 2018 (3)
- November 2018 (4)
- October 2018 (7)
- September 2018 (6)
- August 2018 (5)
- July 2018 (8)
- June 2018 (6)
- May 2018 (5)
- April 2018 (6)
- March 2018 (4)
- February 2018 (6)
- January 2018 (4)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (3)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (4)
- August 2017 (2)
- July 2017 (4)
- June 2017 (5)
- May 2017 (6)
- April 2017 (6)
- March 2017 (5)
- February 2017 (4)
- January 2017 (1)
- July 2016 (3)
- May 2016 (1)
- April 2016 (2)



Comments (1)